Electrical engineering is a vast and diverse field that offers numerous job opportunities in various industries. From designing communication systems for aircraft and spacecraft to developing medical equipment and improving production processes, electrical engineers have a broad range of career paths to choose from. This article will explore the top 10 industries for electrical engineers, including aerospace and defence, energy and power, automotive, construction, telecommunications, healthcare, electronics, robotics, research and development, and manufacturing. Each industry has unique projects and opportunities for electrical engineers to apply their expertise and skills. By understanding the different industries that require electrical engineers, you can identify which career path suits your interests and career goals. Whether you want to work on innovative technologies, develop new products, or improve existing systems, being an electrical engineer offers endless possibilities. In this article, we will delve deeper into each industry, highlighting the roles and responsibilities of electrical engineers and the skills required for success. You can read the summary of post in infographic below or continue down to read the text.
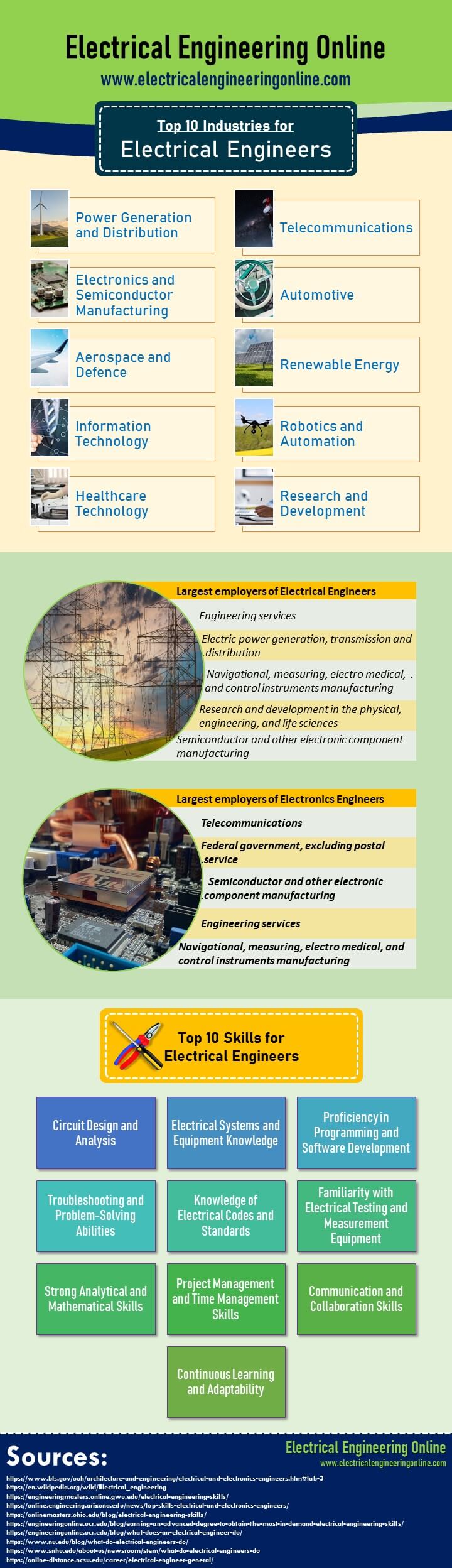
Electrical Power Engineering Industry
The Electrical Power Engineering industry is critical in meeting the energy demands of various residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. The successful operation of the industry relies on the optimal generation, transmission, and distribution of electrical power to ensure a reliable and efficient supply of electricity to end users at economically attractive rates. Electrical Engineers are vital contributors and play a key role in this industry. Electrical Engineers in Power Industry provide their services in planning, designing, operating, maintaining, and optimizing electrical systems and infrastructure to ensure reliable and efficient power supply to consumers. Given below are a few roles and responsibilities of Electrical Engineers in this field:
Power Plant Design and Operation
- Designing, constructing, and operating power plants
- Developing electrical systems in the premises of the plant
- Selecting different power equipment such as generators, transformers, and switchgear
- Ensuring the safe and efficient generation of electricity
Transmission and Distribution Systems
- Designing and maintaining transmission and distribution systems
- Maintaining all substations and distribution stations to ensure transporting electricity from power plants to substations and consumers
Optimizing power flow
- Ensuring reliability and managing voltage regulation
- Grid Infrastructure and Smart Grids
- Contributing to the development and maintenance of electrical grid infrastructure
Integrating renewable energy sources
- Implementing intelligent grid technologies
- Optimizing grid performance and efficiency
System Protection, Operations, and Control
- Ensuring the safety and reliability of the power grid
- Designing and implementing protection systems to detect and mitigate faults
- Developing control systems for efficient power flow management
- Working on grid stability and resilience
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
- Improving the efficiency of power generation and distribution systems
- Analysing energy consumption patterns
- Identifying areas for improvement
- Developing strategies for energy conservation and load management
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Maintaining and troubleshooting power generation and distribution equipment
- Diagnosing electrical faults
- Performing routine maintenance tasks
- Ensuring reliable operation of equipment and systems
Renewable Energy Integration
- Integrating renewable energy systems into the power grid
- Connecting solar farms, wind farms, and other renewable energy sources
- Ensuring the efficient integration of new power systems with the existing power infrastructure
Regulatory Compliance
- Staying updated with electrical codes, standards, and regulations
- Ensuring compliance with safety regulations, environmental standards, and grid interconnection requirements.
Summary: Overall, electrical engineers in the Power Generation and Distribution industry contribute to the planning, design, operation, maintenance, and optimization of electrical systems and infrastructure to ensure a reliable and efficient electricity supply to consumers.
Telecommunication Industry
The telecommunications industry involves transmitting information over long distances using various communication technologies. It encompasses many services, including telephone networks, mobile networks, internet connectivity, satellite communications, etc. This industry plays a vital role in connecting people and enabling the exchange of information globally. In the telecommunications industry, electrical engineers have essential roles in designing, developing, and maintaining the infrastructure and systems necessary for communication. Some specific roles and responsibilities of electrical engineers in the telecommunications industry include:
Network Design and Planning
- Analyze requirements
- Assess network capacity
- Determine optimal layout and architecture for efficient communication
Signal Processing
- Develop algorithms
- Design filters
- Analyze data transmission methods
Network Equipment Development
- Contribute to hardware and software design
- Ensure functionality, reliability, and compatibility with network standards
System Integration
- Connect different network components
- Ensure seamless communication and interoperability between different systems and protocols
Network Security
- Implement and maintain network security measures
- Work on encryption techniques, firewall configurations, and intrusion detection systems
Network Optimization and Performance Monitoring
- Analyze network traffic
- Identify bottlenecks
- Implement solutions to enhance network efficiency, capacity, and reliability
Testing and Troubleshooting
- Perform testing and troubleshooting of telecommunication systems and equipment
- Use specialized tools and equipment to diagnose and resolve technical issues
Regulatory Compliance
- Stay updated with regulatory requirements and standards related to telecommunications
- Ensure compliance with legal and safety regulations for telecommunication systems and infrastructure
Above are just a few examples of electrical engineers’ roles in the telecommunications industry. The industry continues to evolve rapidly, introducing new technologies like 5G and future trends like 6G, the Internet of Things (IoT), and fiber optics, creating further opportunities for electrical engineers to contribute to its development and innovation.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing industry
The Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing industry encompasses the production of electronic devices, components, and integrated circuits (semiconductors). This industry plays a crucial role in modern technology, as electronic devices are essential in various sectors, such as telecommunications, consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and more. In the Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing industry, electrical engineers have several important roles and responsibilities:
Circuit Design
- Designing electronic circuits and systems, including integrated circuits (ICs)
- Create efficient and reliable circuit designs
Testing and Verification
- testing and verification of electronic devices and components
- To ensure that design meets quality and performance standards
- Develop and implement testing methodologies
- Conducting various tests
- Analysing data and troubleshoot issues
Process Development and Improvement
- Develop and improve electronics manufacturing processes
- Improve overall systems used for designing electronic devices and semiconductors
- Optimizing production methods, reducing costs, increasing yield, and enhancing overall efficiency
Equipment Maintenance and Calibration
- Maintaining, calibrating, and troubleshooting manufacturing equipment used in electronic and semiconductor production
- Ensuring that equipment functions correctly
- Performing repairs when needed
- Ensuring accurate measurement and control
Quality Control and Assurance
- Developing and implementing quality control measures
- Ensuring that the manufactured electronic devices and components meet the required specifications and standards
Research and Development
- Using technical knowledge to research and development in the electrical engineering industry
- Exploring new technologies, materials, and techniques in the electrical field
- Develop methods to enhance electronic devices’ and semiconductor components’ performance and functionality
Collaboration with Cross-functional Teams
- Collaborating with professionals from other disciplines, such as mechanical engineers, software engineers, and manufacturing specialists for integration of electronics in other systems
- Working with teams together to integrate electrical components into larger systems, ensure compatibility, and address any interdisciplinary challenges.
Overall, electrical engineers in the Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing industry play a critical role in designing, testing, improving manufacturing processes, and ensuring the quality of electronic devices and semiconductor components. They contribute to advancing technology, improving efficiency, and meeting the growing demands of the electronics market.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry encompasses the design, development, manufacturing, and maintenance of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other types of motor vehicles. The role of electrical engineers in the automotive industry has become increasingly important as vehicles have evolved to incorporate advanced electronics and electrical systems. Electrical engineers in the automotive industry are responsible for designing and testing vehicle electrical systems, ensuring their safety, and improving efficiency. They are crucial in advancing vehicle technology and making them more sustainable and environmentally friendly. Here are some key areas where electrical engineers contribute to the automotive industry:
Vehicle Electronics
- Designing and developing various vehicle electronic systems including powertrain control modules, engine management systems, body control modules, infotainment systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS)
- They work on integrating, programming, and testing these systems to ensure proper functionality and performance.
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
- Developing electrical architecture, including high-voltage systems, battery management systems, charging infrastructure, and regenerative braking systems.
- Optimizing energy efficiency, battery performance, and overall system integration
Embedded Systems and Software
- Developing embedded systems and software that control various vehicle functions
- Programming microcontrollers
- Implementing engine control
- Working on Transmission control, braking, steering, and sensor integration algorithms
Vehicle Networking and Communication
- Designing and implementing vehicle networking systems, such as Controller Area Networks (CAN) and Ethernet
- Facilitating communication between different electronic components within the vehicle
Safety and Security Systems
- Design and implement safety systems in vehicles
- Including airbag systems
- Antilock braking systems (ABS)
- Electronic stability control (ESC)
- ADAS features like adaptive cruise control
- Lane departure warning
- Collision avoidance
- Cyber security systems
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
- Providing assistance in developing diagnostic tools and systems
- Identification and troubleshooting electrical and electronic faults in vehicles
- Carrying out onboard diagnostic (OBD) systems
- Integrating diagnostics capabilities into vehicle software
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
- Ensuring that vehicle electrical systems comply with relevant industry standards and regulations for safety, emissions, and performance
- Staying up to date with evolving regulations and work to implement necessary changes in the electrical systems
Electrical engineers within the automotive industry play an essential role in designing, developing, integrating, and maintaining various electrical and electronic systems found in vehicles. Their expertise is paramount in advancing vehicle technology, improving performance, enhancing safety, and meeting industry standards.
Aerospace and Defence
The Aerospace and Defence industry encompasses the design, development, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, missiles, and other defence-related systems. It is a technologically advanced sector focusing on civilian and military applications.
The Aerospace and Defence industry is a technologically advanced sector that includes designing, developing, manufacturing, and maintaining aircraft, spacecraft, missiles, and other defence-related systems. This industry focuses on both civilian and military applications and requires the contributions of electrical engineers in various areas, such as:
Electrical engineers play a crucial role in the Aerospace and Defence industry by applying their expertise in various areas.
Avionics Systems Engineering
- Design, development, and integration of avionics systems
- Ensuring efficient and reliable operation of communication systems, navigation systems, flight control systems, and instrumentation
- Meet stringent safety and performance standards
Embedded Systems Engineering
- Working on embedded systems for control and monitoring functions in aerospace and defence applications
- Develop and program embedded software to control subsystems such as flight control systems, engine management systems, and mission-critical components
Aircraft Power Systems Engineer
- Design and develop power generation and distribution systems for aircraft, spacecraft, and other defence platforms
- Focus on optimizing power efficiency, managing power demands, and ensuring the availability of reliable power for various systems and equipment
RF and Communication Systems Engineer
- Contribute to the design, development, and implementation of communication systems used in aerospace and defence applications
- Work on radar systems, satellite communication systems, wireless communication technologies, and antenna systems
Control Systems Engineer
- Work on flight control systems
- Designing guidance systems, and autonomous systems in aerospace and defence
- Develop algorithms
- Design control systems
- Ensure stability and precision in the operation of aircraft
- Working on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and missile systems
System Integration Engineer
- Working on system integration
- Integrating various electrical and electronic components and subsystems
- Complex aerospace and defence systems
- Ensuring proper functionality, compatibility, safety, and performance requirements compliance.
These are just a few examples of electrical engineers’ roles in the Aerospace and Defence industry. They contribute to the development of cutting-edge technologies, ensure system reliability and safety, and enable the successful operation of advanced aerospace and defence systems.
Renewable Energy Industry
Renewable resource refers to the resource for which there is an endless supply because it can be replenished. The renewable energy industry focuses on generating electricity from renewable sources such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. It aims to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the environmental impacts of conventional energy generation. Electrical engineers play a vital role in this industry, contributing their expertise in electrical systems, power electronics, grid integration, and control systems. Their key contributions include:
System Design
- Determine the optimal configuration of components for renewable energy systems, considering factors like power output, efficiency, and integration with the electrical grid.
Power Electronics and Conversion
- Design and develop power electronics systems for renewable energy applications, working on inverters, converters, and controllers that efficiently manage power flow.
Grid Integration
- Facilitate the integration of renewable energy systems with existing power grids, ensuring proper synchronization, voltage regulation, and grid stability.
Energy Storage
- Developing energy storage systems
- Optimizing charging and discharging processes
- Designing control systems
- Ensuring seamless integration with renewable energy systems
Monitoring and Control
- Implementing monitoring and control systems for renewable energy installations
- Developing SCADA systems
- Working on advanced control algorithms
- Working on remote monitoring solutions
Grid Resilience and Microgrids
- Designing resilient power systems incorporating renewable energy sources
- Creating micro grids that operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid.
Research and Development on renewable technologies
- Contributing to research and development activities in renewable energy
- Exploring new technologies, materials, and
- Researching the system architectures to enhance efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness
Electrical engineers are vital in advancing renewable energy technologies and driving the transition to clean and sustainable energy sources. They contribute their expertise in electrical, power electronics, grid integration, and control systems to make renewable energy a viable and integral part of the global energy landscape.
Electrical engineers’ contributions are crucial in advancing renewable energy technologies and driving the transition to clean and sustainable energy sources. They are pivotal in making renewable energy a viable and integral to the global energy landscape.
Information Technology
Information Technology (IT) refers to using, developing, and managing computer-based systems, software, and networks to store, process, transmit, and retrieve information. It encompasses various technologies and applications that enable businesses and individuals to manage and utilize data effectively.
Information Technology (IT) refers to using, developing, and managing computer-based systems, software, and networks to store, process, transmit, and retrieve information. In the field of IT, electrical engineers play a vital role in various aspects, including:
In IT, electrical engineers play a critical role in different aspects. Here are some key areas where electrical engineers contribute:
Network Infrastructure
- Design, implement, and maintain electrical and electronic components
- Ensuring efficient data transmission, network security, and reliable connectivity
Data Centres
- Designing and manage the electrical systems of data centres
- Working on power distribution, backup power systems, cooling systems, and other electrical aspects
- Ensuring the smooth and uninterrupted operation of servers and equipment
Hardware Development
- Designing and developing hardware components for IT systems
- Working on circuit boards, processors, memory modules, and other electronic components
- Enhancing performance, optimizing power consumption, and ensuring compatibility with software and systems.
Embedded Systems
- Contribute to designing, programming, and testing embedded systems used in IT-related products
- Working on embedded circuits and products in smartphones, tablets, wearable’s, and IoT devices.
Software and Firmware
- Participating in software and firmware development for IT systems
- Working on programming and coding aspects related to hardware interfaces, device drivers, and low-level system functionalities
- Ensuring smooth interaction between software and hardware components
Power Management
- Working on IT systems’ power management and energy efficiency
- Dealing with optimizing power distribution, reducing power losses, and implementing energy-saving measures
- Enhancing the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of IT infrastructure
Research and Innovation
- Contributing to research and development efforts in IT
- Exploring new technologies, design novel systems, and improve existing solutions.
- Helping to advance IT capabilities, address emerging challenges, and drive innovation in networking, computing, and communication.
It’s worth noting that the specific role of an electrical engineer in IT may vary based on their specialization, such as power systems, electronics, or telecommunications. The convergence of electrical engineering and IT has created numerous opportunities for professionals with expertise in both domains to contribute to developing and advancing IT infrastructure and applications.
Robotics and Automation Industry
The Robotics and Automation industry focuses on developing, implementing, and operating automated systems and robotic technologies. It involves creating machines and systems that can perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. These technologies are used in various sectors, such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, etc.
The Robotics and Automation industry involves developing, implementing, and operating automated systems and robotic technologies. These technologies are used in various sectors, such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, etc. Electrical engineers play a crucial role in the Robotics and Automation industry by contributing their expertise in several areas:
System Integration
- Integrating various components and subsystems within a robotic system
- Ensuring that the electrical components, such as sensors, actuators, motors, and controllers, work together seamlessly
Control Systems
- Designing and implementing control systems that enable robots to perform precise and coordinated movements
- Developing algorithms and programming logic to make the robot sense and respond to its environment effectively
Sensor Integration
- Work on integrating different types of sensors, such as vision systems, proximity sensors, force sensors, and others, to provide robots with accurate and real-time feedback.
Motor Control
- Designing and implementing motor control systems that enable precise movement and manipulation of robotic systems
- Working with different types of motors, such as servo, stepper, and DC motors, to achieve desired motion and speed control.
Power Supplies
- Working on power supplies that provide the required voltage levels, current capacities, and backup mechanisms to ensure the uninterrupted operation of robotic systems
Safety and Compliance
- Ensure that robotic systems meet safety standards and regulations
- Design safety features, such as emergency stop systems and interlocks
- Integrating all safety systems to prevent accidents and protect human operators and nearby personnel
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Diagnose and repair electrical faults
- Calibrate sensors and control systems
- Optimize the performance of robots
Overall, electrical engineers play a vital role in the Robotics and Automation industry by designing, developing, and maintaining the electrical systems that power and control robotic technologies. Their expertise ensures the efficiency, reliability, and safety of automated systems.
Healthcare Technology
The Healthcare Technology industry applies technology and engineering principles to improve healthcare delivery, enhance patient care, and advance medical research. It encompasses various areas such as medical devices, diagnostic equipment, healthcare information systems, telemedicine, and medical imaging. In this industry, electrical engineers play a crucial role in developing, designing, and maintaining the electrical systems and technologies used in healthcare settings. Some specific roles and responsibilities of electrical engineers in the Healthcare Technology industry include:
Medical Device Design
- Circuit design
- Embedded systems
- Sensor integration
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards
Biomedical Instrumentation
- Signal processing
- Data acquisition
- Integration of sensors
Healthcare Information Systems
- Data management
- Network Infrastructure
- Cybersecurity
- Interoperability
Medical Imaging
- Image reconstruction algorithms
- Signal processing
- Hardware design
- Image quality optimization
Healthcare Infrastructure
- Power distribution
- Lighting
- Emergency backup systems
- Safety measures
Regulatory Compliance
- Ensuring medical devices and systems meet regulatory requirements
- To ensure that device meet all appliable local and international standards
Overall, electrical engineers contribute to developing innovative healthcare technologies, improving patient outcomes and supporting medical professionals in their work. Their expertise in electrical systems, circuit design, instrumentation, and software development is essential in advancing healthcare technology and its integration into healthcare settings.
Research and Development
The Research and Development (R&D) industry encompasses organizations and activities focused on scientific research, innovation, and developing new technologies, products, and processes. Electrical engineers play a crucial role in advancing technology and creating new solutions in this industry. Their specific contributions can vary depending on the organization and project, but here are some typical roles and responsibilities for electrical engineers in the R&D industry:
Technology Research
- To participate in researching emerging technologies, trends, and advancements in their field.
Conceptualization and Design
- Electrical engineers are involved in the conceptualization and design of new products, systems, or components
Prototyping and Testing
- Electrical engineers play a key role in building prototypes and testing new ideas.
Data Analysis and Modelling
- Employ mathematical modelling and data analysis techniques
- Evaluate the performance and behaviour of new technologies or systems.
Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Work
- Collaborate with professionals from various disciplines, such as mechanical engineers, computer scientists, and material scientists, to develop innovative solutions.
Documentation and Reporting
- Documenting the technical work
- Documenting the design specifications
- Keeping and maintaining testing procedures, and research findings
Intellectual Property and Patents
- Conducting patent searches
- Assessing intellectual property landscape
- Contributing to the patent application process to protect the organization’s innovative technologies
Collaboration with Universities and Research Institutions
- Collaborate with universities and research institutions to leverage their resources
- Access specialized knowledge
- Collaborate and coordinate on cutting-edge research projects.
Overall, electrical engineers in the R&D industry play a critical role in pushing the boundaries of technology, driving innovation, and bringing new ideas to life. Their expertise and contributions are instrumental in developing breakthrough technologies and shaping the future of various industries.
Sources
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/architecture-and-engineering/electrical-and-electronics-engineers.htm#tab-3
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_engineering
- https://engineeringmasters.online.gwu.edu/electrical-engineering-skills/
- https://online.engineering.arizona.edu/news/top-skills-electrical-and-electronics-engineers/
- https://onlinemasters.ohio.edu/blog/electrical-engineering-skills/
- https://engineeringonline.ucr.edu/blog/earning-an-advanced-degree-to-obtain-the-most-in-demand-electrical-engineering-skills/
- https://engineeringonline.ucr.edu/blog/what-does-an-electrical-engineer-do/
- https://www.nu.edu/blog/what-do-electrical-engineers-do/
- https://www.snhu.edu/about-us/newsroom/stem/what-do-electrical-engineers-do
- https://online-distance.ncsu.edu/career/electrical-engineer-general/
